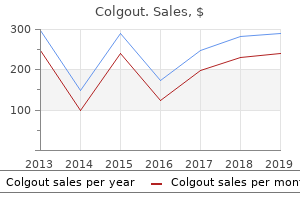
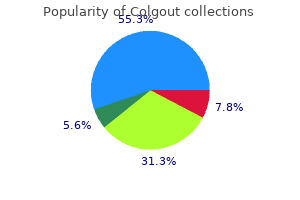
"Order colgout cheap online, antibiotics for acne online".
By: K. Thorus, M.S., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Midwestern University Chicago College of Osteopathic Medicine
In the bloodstream there are two pools usually of about equal size: the circulating pool (included in the blood count) and the marginating pool (not included in the blood count) antibiotics for dogs home remedy buy colgout 0.5mg on line. Control of granulopoiesis: myeloid growth factors the granulocyte series arises from bone marrow progenitor cells which are increasingly specialized virus ny generic colgout 0.5 mg on line. The growth factors stimulate proliferation and differentiation and also affect the function of the mature cells on which they act antimicrobial qualities cheap 0.5mg colgout visa. This may translate into a reduction of length of time in hospital antimicrobial use buy cheap colgout online, antibiotic usage and frequency of infection but periods of extreme neutropenia after intensive chemotherapy cannot be prevented. Their extravascular lifespan after their transformation to macrophages (histiocytes) may be as long as several months or even years. The leucocyte adhesion molecules also mediate recruitment, migration and interaction with other immune cells. They are also variously expressed on endothelial cells and platelets (see Chapter 1). Disorders of neutrophil and monocyte function the normal function of neutrophils and monocytes may be divided into three phases. Chemotaxis (cell mobilization and migration) the phagocyte is attracted to bacteria or the site of inflammation by chemotactic substances released the foreign material. Recognition of a foreign particle is aided by opsonization with immunoglobulin or complement because both neutrophils and monocytes have Fc and C3b receptors (see Chapter 9). They also secrete a large number of growth factors and chemokines that regulate inflammation and immune responses. Chemokines may be produced constitutively and control lymphocyte traffic under physiological conditions; inflammatory chemokines are induced or up-regulated by inflammatory stimuli. They bind to and activate cells via chemokine receptors and play an important part in recruiting appropriate cells to the sites of inflammation. Killing and digestion this occurs by oxygen-dependent and oxygenindependent pathways. In neutrophils, H2O2 reacts with myeloperoxidase and intracellular halide to kill bacteria; activated oxygen may also be involved. They may also act with a fall in pH within phagocytic vacuoles into which lysosomal enzymes are released. An additional iron binding protein, lactoferrin, is present in neutrophil granules and is bacteriostatic by depriving bacteria of iron and generating free radicals. Defects of phagocytic cell function Chemotaxis these defects occur in rare congenital abnormalities. On entering the neutrophil, the bacterium is surrounded by an invaginated surface membrane and fuses with a primary lysosome to form a phagosome. Secondary granules also fuse with the phagosomes, and new enzymes from these granules including lactoferrin attack the organism. Various types of activated oxygen, generated by glucose metabolism, also help to kill bacteria. Killing this abnormality is clearly illustrated by the rare X-linked or autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous disease that results from abnormal leucocyte oxidative metabolism. There is an abnormality affecting different elements of the respiratory burst oxidase or its activating mechanism. The patients have recurring infections, usually bacterial but sometimes fungal, which present in infancy or early childhood in most cases. Other rare congenital abnormalities may also result in defects of bacterial killing.
It is often associated with ascites or ascites and pleural effusion (Demons-Meigs syndrome) which regresses after surgical removal antibiotic diarrhea treatment order genuine colgout online. Benign Brenner Tumor this surface epithelial-stromal tumor of transitional cells (resembling urinary bladder epithelium) is of very rare occurrence; it affects mainly women in the fifth and sixth decade infection viral 0.5mg colgout with amex. Nonetheless antibiotics for uti augmentin colgout 0.5 mg discount, laparoscopic inspection alone of the adnexae often allows the surgeon to make a benign-malignant differentiation zombie infection pc order colgout amex. Pelvic pain is the most frequent symptom although asymptomatic patients are not rare. In fact, it is only when the cysts reach a considerable size and produce pain in the ipsilateral iliac fossa that they become apparent and spur the patient to consult a doctor. Rarely, the pelvic pain can present as an acute abdomen, secondary to rupture of a cyst or ovarian torsion. In advanced malignant disease, patients complain of abdominal distension, swelling, constipation, nausea and anorexia. Deep palpation reveals the outline, consistency, increased volume and mobility of the adnexal mass. Benign Adnexal Mass It can be considered benign when a unilateral, mobile swelling with a smooth surface is found on examination. Adnexal Mass Suspicious for Malignancy A fixed mass with irregular margins, possibly bilateral, raises the suspicion of a malignant ovarian neoplasm. Benign Adnexal Mass the ultrasonic characteristics that suggest a benign nature of the lesion include: size < 6 cm, unilocular structure, homogeneous contents, absence of internal proliferations and Manual of Gynecologic Laparoscopic Surgery 157 septa (possibly thin ones, < 2-3 mm), presence of smooth walls and well-defined margins. Hemorrhagic cysts can contain internal echoes of variable intensity, both focal and diffuse. Adnexal Mass Suspicious for Malignancy the presence of bilateral masses with irregular margins, multiple thick intracyst septa (> 4 mm), papillary projections, solid areas and the presence of ascites raise the suspicion of a malignant ovarian neoplasm. The muscle layer of the walls of these vessels is reduced so resistance to blood flow is low. Quantification of the blood flow impedance and the presence, distribution and architecture of neovascularization inside the adnexal mass can be utilized in the differential diagnosis of these lesions. However, color Doppler studies can give false-negative results due, for example, to areas of avascular necrosis in malignant tumors. Conversely, complex adnexal masses with a solid and vascularized part (dermoid cysts, Brenner tumors) can give false-positive results. Because of their low specificity and sensitivity, the tumor markers may only be used as an adjunct measure for predictive purposes that can help to differentiate benign from malignant adnexal masses. Surgical therapy must thus be tailored to the individual case, applying the basic principle of preserving as much ovarian tissue as possible. The advantages of laparoscopy are obvious when applied to establish a differential diagnosis in terms of the benign/malignant nature of the adnexal mass. In young women who wish to preserve their fertility, laparoscopy allows intraoperative biopsies to be taken from the ovarian surface without causing rupture of the cyst. In the presence of a suspicious adnexal mass, intraoperative laparoscopic assessment may assist in choosing the type of abdominal incision, which should extend from the xiphoid process to the pubic symphysis in the presence of a malignant neoplasm. En-bloc enucleation of an endometrioma, a mucinous cyst or ovarian lesion larger than 10 cm is very difficult to manage laparoscopically. Under the aforementioned conditions, it is preferable to perform controlled prophylactic aspiration rather than risk accidental spillage of the cyst contents due to rupture, which occurs frequently. Above all, cyst aspiration facilitates cystectomy by reducing the tension of the cyst and allows inspection of its internal walls. The suction cannula is introduced directly into the cyst on the antimesenteric side after immobilizing the ovary, grasping the ovarian ligament with an endoclinch grasping forceps. After removing the cyst contents with a suction cannula, the cyst cavity is lavaged. It is then possible to introduce the laparoscope through the opening to assess the inner surface. It is surprising how often it is possible even with large cysts to preserve sufficient ovarian tissue around the hilum to restore ovarian anatomy satisfactorily. If an adequate blood supply can be ensured, full recovery of organ function can be anticipated. Technique in brief To improve exposure of the adnexae, a uterine manipulator must be applied. The ovary is then mobilized by lysis of the paraphysiological adhesions to the rectosigmoid.
Best buy for colgout. Antibiotics for Gram Negative Infections (Antibiotics - Lecture 5).
When I saw this acknowledgment antimicrobial socks cheap colgout online, I wondered what exactly these persons had done (family names are fictitious): We thank C antimicrobial herbs and phytochemicals effective 0.5 mg colgout. In the following example it is evident what each person did: We thank Betsy Roe and Gerri Doe for their assistance in preparing the data; William Poe for the medical photography; Marian Loe and David Coe for their critique of the findings of this study; and Fred Noe for reviewing the 200- m and 400-m specimens antibiotics for acne bad buy colgout 0.5mg fast delivery. Persons you want to thank should be asked if they are willing to be acknowledged and if they approve the wording you have Acknowledgements 79 used to mention them infection medicine buy colgout 0.5 mg cheap. This is because colleagues who have read and corrected your manuscript may disagree with some of its central points. Always give credit for financial support When you thank sources of financial assistance, be careful how you present their names. But do not thank all grant-giving agencies who have supported your research work over several years past. Thank only those which supported the study you are now reporting because, just as research teams compete with one another, so too do granting authorities. And if one authority alone has chosen and supported a promising work, you should give that authority all due credit. Note that some journals ask that funding organizations be named on the title page instead of being included in the acknowledgments. The editors of some major biomedical journals therefore had good reason to convene in Vancouver, Canada, in January 1978, to work out a uniform reference style. One of their suggestions was that authors should number references in the order in which they appear in the text (International Committee of Medical Journal Editors 1997). In the fictive sentence below, I have mixed the two styles to illustrate their differences: A reference figure (17) in the Vancouver style says less than a name-and-year reference (Einstein 1941) according to the Harvard system. Most readers prefer the Harvard system because they like to know just what author is being cited as they read the text. Using the Vancouver system, the text above can be condensed to about one-third of its original length: this method was introduced by Aburel in 1938,1 but he was followed by only a few workers in the succeeding 20 years. Nevertheless, you have to follow the style of the journal to which the paper is to be submitted. By using a suitable computer program you can, at the touch of a few keys, produce reference lists in the format of your choice and, in the text, substitute names for numbers (or vice versa). I also take the opportunity to show how to refer to unpublished results and personal communications. In some submitted papers as many as every second reference was untraceable by direct search. The number of errors can be reduced by checking and rechecking not only new references but also those lifted from your own computer bank of citations. However, citing a publication you have not seen can be hazardous, as the following illustrates. He was assumed to be the author of a Czech-language article, reporting the first experiments in which amebic dysentery was transmitted from man to cat. Hence, if you refer to a paper you have not read, say so: Amebic dysentery was successfully transmitted from man to cat (Uplavici 1887, cited by Kartulis 1887). The citation of abstracts is particularly to be discouraged, as only about one-third of them lead to full-length, peer-reviewed articles (Liu 1996). Your own author name Decide early in your career the form in which you wish your name to appear. If you have a common name, it may be wise to use your middle initials in order to be distinguished from other scientists. If you change your surname and start using the new name as your author name, your previous scientific work will become hard to trace. So, stick to the name under which you wrote or coauthored your first papers (van Loon 1997).
B cells recognize antigen through their surface immunoglobulin and although most antibody responses require help from antigenspecific T cells infection heart 0.5 mg colgout visa, some antigens such as polysaccharides can lead to T-cell independent antibody production antibiotics for staph buy cheap colgout 0.5mg on line. T cells are screened for recognition of antigen and if a T cell makes an interaction it migrates into the follicle antibiotic quinine cheap colgout 0.5 mg fast delivery. In the follicle antimicrobial agents antibiotics generic colgout 0.5mg mastercard, germinal centres arise as a result of continuing response to antigenic stimulation. Proliferating B cells move to the dark zone of the germinal centre as centroblasts where they undergo somatic mutation of their immunoglobulin variable-region genes. Although they contain intracellular immunoglobulin they do not express surface immunoglobulin. Lymphocytosis Lymphocytosis often occurs in infants and young children in response to infections that produce a neutrophil reaction in adults. Glandular fever is a general term for a disease characterized by fever, sore throat, lymphadenopathy and atypical lymphocytes in the blood. The disease is associated with a high titre of heterophile (`reacting with cells of 136 / Chapter 9 White cells: Lymphocytes Lymph from extravascular tissue space Afferent lymphatics Primary follicle Subcapsular sinus Marginal zone Follicles (B cells) T zone Medullary cord Germinal Secondary centre Mantle follicle zone Efferent lymphatics Lymph returned to venous blood (a) (b) Figure 9. Clinical features the majority of patients are between the ages of 15 and 40 years. A prodromal period of a few days occurs with lethargy, malaise, headaches, stiff neck and a dry cough. In established disease the following features may be found: 1 Bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy is present in 75% of cases. B cells activated by antigen migrate from the T zone to the follicle where they undergo massive proliferation. Cells enter the dark zone as centroblasts and accumulate mutations in their immunoglobulin V genes. Only those cells that can interact with antigen on follicular dendritic cells and receive signals from antigen-specific T cells. Diagnosis Pleomorphic atypical lymphocytosis A moderate rise in white cell count. These T cells are 138 / Chapter 9 White cells: Lymphocytes (a) (b) (c) (d) Figure 9. The greatest number of atypical lymphocytes are usually found between the seventh and tenth day of the illness. Heterophile antibodies Heterophile antibodies against sheep or horse red cells may be found in the serum at high titres. Modern slide screening tests, such as the monospot test, use formalinized horse red cells to test for the IgM antibodies that agglutinate the cells. Highest titres occur during the second and third week and the antibody persists in most patients for 6 weeks. Haematological abnormalities Haematological abnormalities other than the atypical lymphocytosis are frequent. Thrombocytopenia is frequent and an autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura occurs in a smaller number of patients. Treatment In the great majority of patients only symptomatic treatment is required. Patients characteristically develop an erythematous rash if given ampicillin therapy. However, convalescence may be slow and associated with severe malaise and lethargy. Lymphopenia Lymphopenia may occur in severe bone marrow failure, with corticosteroid and other immunosuppressive therapy, in Hodgkin lymphoma and with widespread irradiation. Immunodeficiency A large number of inherited or acquired defects in any of the components of the immune system can cause an impaired immune response with increased susceptibility to infection (Table 9. In some cases, however, lack of specific subsets of T cells which control B-cell maturation may lead to a secondary lack of B-cell function, as in many cases of common variable immunodeficiency, which may develop in children or adults of either sex. X-linked agammaglobulinaemia is caused by failure of B-cell development; pyogenic bacterial infections dominate the clinical course. Immunoglobulin replacement therapy can be given by monthly courses of intravenous immunoglobulin. Rare syndromes include aplasia of the thymus, severe combined (T and B) immunodeficiency as a result of adenosine deaminase deficiency and selective deficiencies of IgA or IgM. Immunodeficiency is also frequently associated with tumours of the lymphoid system including chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and myeloma.