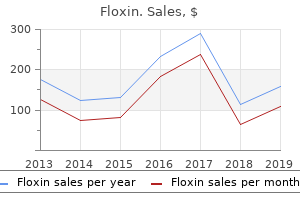
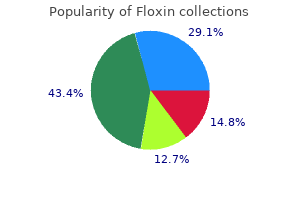
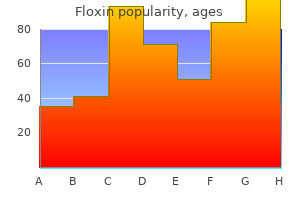
"Buy floxin with american express, bacteria nucleus".
By: P. Uruk, M.B.A., M.D.
Professor, University of Oklahoma School of Community Medicine
In mice antibiotics for acne philippines 400mg floxin with mastercard, B1a cells seem to be essential for the production of natural antibodies that provide protection against encapsulated bacteria treatment for glaucoma dogs cheap 400 mg floxin otc, whereas B1b cells are essential for producing anticapsular antibodies in response to immunization [953] usp 51 antimicrobial effectiveness test order 400mg floxin mastercard. It is unclear whether the frequency antimicrobial use in food animals discount generic floxin uk, distribution, and function of B-1 cells differ in the human fetus and neonate compared with the adult; this requires the development of new markers that can distinguish human B-1 cells from B-2 cells. In mice, B-1 cells constitute the major source of the low amounts of circulating "natural" IgM present at birth produced in the absence of antigenic stimulation, and animals lacking the ability to secrete natural IgM have an increased susceptibility to acute peritonitis from endogenous bacteria [959]. In addition to a role in host defense, natural IgM may also play a role in removing apoptotic cells [847]. As discussed subsequently ("Immunoglobulin Synthesis by the Fetus and Neonate"), total circulating IgM is very low in the fetus and healthy newborn. Some autoreactivity was observed with cord blood IgA, although to a much lesser degree than for IgM. The importance of natural IgM in human host defense in the fetus and neonate and its B-cell source is unclear. The antibody response to T-dependent antigens is characterized by the generation of memory B cells with somatically mutated, high-affinity immunoglobulin and the potential for isotype switching. T-independent type I antigens are antigens that bind to B cells and directly activate them in vitro to produce antibody without T cells or exogenous cytokines. Most studies of the neonatal immune response to T-dependent antigens have not evaluated antibody affinity, a reflection of somatic mutation, or isotype expression. This reduction may reflect a decreased ability of antigen-activated B cells to proliferate, rather than a decreased precursor frequency of antigen-specific clones [970]. In fetal sheep, the antibody response to bacteriophage jX174 occurs 40 days after conception [975], and isotype switching is evident during the fetal response. Together, these findings suggest that the B-cell responses to protein antigens, including isotype switching and probably memory cell generation, are functional during fetal life. Second, these responses occur in a predictable, stepwise fashion for particular antigens. In fetal sheep, the antibody responses to keyhole limpet hemocyanin and lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus are first detectable at about 80 and 120 days after conception [975]. No correlation exists between the physical or chemical characteristics of particular antigens and their immunogenicity during ontogeny. In fetal sheep, however, bacteriophage T4 becomes immunogenic 60 days after jX174 does so. The response to some vaccines may be less vigorous in the neonate, however, than in older children or adults. If initial immunization is delayed until 1 month of age, the antibody response to primary hepatitis B vaccination is increased and nearly equivalent to that in older children, suggesting that the developmental limitations responsible for reduced antibody responses are transient [993,995]. Similarly, 2-week-old infants immunized with a single dose of diphtheria or tetanus toxoid showed delayed production of specific antibody compared with older infants, but by 2 months of age, their response was similar to the response of 6-month-old infants [996]. The switch from IgM to IgG also may be delayed after neonatal vaccination for some. Whole-cell pertussis vaccine immunization of premature infants (born at 28 to 36 weeks of gestation) at 2 months of age elicited responses similar to those in 2-month-old term infants [989], indicating that this putative tolerigenic period wanes rapidly and is relatively independent of gestational age. This low-level tolerance was restricted to the pertussis component of the whole-cell pertussis vaccine because an inhibitory effect has not been observed after administration of diphtheria or tetanus toxoid [988] or hepatitis B vaccine given within 48 hours of birth [993].
It is believed that this subspecies rarely is found in the human intestine and that it is not a cause of human enteritis [739] antibiotics for uti erythromycin buy floxin with mastercard. A nosocomial nursery outbreak has been associated with carriage in some healthy infants [845] how antibiotics for acne work generic 200mg floxin otc. Cervical cultures have remained positive in women who have had recurrent abortions and whose husbands have antibody titer elevations [752] antimicrobial laundry additive generic floxin 200 mg on line. This occurred in some instances despite the use of tetracycline antibiotic resistance timeline best buy for floxin, to which Campylobacter was susceptible in vitro, in the chicken feed [842]. Because Campylobacter infections of the udder are not seen, milk is probably contaminated from fecal shedding of the organism. Extraintestinal manifestations generally occur in patients who are immunosuppressed or at the extremes of age [727]. Diagnosis Most important in the diagnosis of Campylobacter infection is a high index of suspicion based on clinical grounds. Isolation of Campylobacter from blood or other sterile body sites does not represent the same problem as isolation from stool. A high index of suspicion and prompt, appropriate antimicrobial therapy may prevent the potentially serious neonatal complications that may follow maternal C. It is a fastidious, microaerophilic, curved, motile gram-negative bacillus that has a single polar flagellum and is oxidase and catalase positive except for C. It grows on various media, including Brucella and Mueller-Hinton agars, but optimal isolation requires the addition of selective and nutritional supplements. Growth at 42 C in the presence of cephalosporins is used to culture selectively for C. In a study of six media, charcoal-based selective media and a modified charcoal cefoperazone deoxycholate agar were the most selective for identification of Campylobacter species. Extending the incubation time from 48 to 72 hours led to an increase in the isolation rate regardless of the medium used [871]. Its typical darting motility may provide a clue to identification, even in fresh fecal specimens, when viewed by phase-contrast microscopy [735,872]. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes are usually found in stools when bloody diarrhea occurs and indicate the occurrence of colitis [776,812]. These infected neonates, who are often premature, develop signs suggesting sepsis, including fever, cough, respiratory distress, vomiting, diarrhea, cyanosis, convulsions, and jaundice. The condition typically progresses to meningitis, which may be rapidly fatal or may result in serious neurologic sequelae [725]. Additional systemic manifestations include pericarditis, pneumonia, peritonitis, salpingitis, septic arthritis, and abscesses [837]. Older infants and children generally are affected, but neonates with diarrhea have been reported. Stools can contain blood, mucus, and pus [725,735,776,777]; fever often is absent [735,776]. The illness usually responds to appropriate antimicrobial therapy [774,776,830], which shortens the period of fecal shedding [859]. Meningitis that apparently occurs secondary to intestinal infection also has been reported in premature infants who have had intraventricular needle aspirations for neonatal hydrocephalus [725]. Diagnostic considerations for inflammatory or bloody enteritis include necrotizing enterocolitis, allergic proctitis, and Salmonella; rarely Shigella and other infectious agents occur. Infected food handlers and hospital employees who are asymptomatic pose no known hazard for disease transmission if proper personal hygiene measures are maintained. Both toxin genes have been cloned and sequenced, revealing that they encode proteins with estimated molecular masses of 308 kDa for toxin A and 270 kDa for toxin B [884]. A wide variety of antibacterial, antifungal, antituberculosis, and antineoplastic agents have been associated with C.
A more recent study among infants 0 to 3 months old from Bangladesh showed that breastfeeding provided significant protection against diarrheal disease with an adjusted odds ratio of 0 infection in bone discount floxin online master card. Protection afforded by breast-feeding against diarrhea during the first months of life has also been observed in more industrialized societies such as the United Kingdom [62] virus 36 buy discount floxin online. Multiple mechanisms by which breast-feeding protects against diarrhea have been postulated antibiotic 3 times a day purchase 200mg floxin mastercard. Breast-feeding confers protection by active components in milk and by decreased exposure to organisms present on or in contaminated bottles antimicrobial incise drape buy discount floxin 200mg, food, or water. Redundancy of milk protective factors and targeting of complex virulence machinery have created a formidable barrier to enteropathogens. Despite the fact that pathogens can rapidly divide and mutate, milk continues to protect infants. Human milk has secretory antibodies to Shigella virulence antigens and lipopolysaccharides [66,67], neutral glycolipid Gb3 to bind Shiga toxin [68,69], and lactoferrin to disrupt and degrade the surface-expressed virulence antigens. Human milk can initiate and maintain the growth of Bifidobacterium species and low pH in the feces of newborn infants, creating an environment antagonistic to the growth of E. Lysozyme in human milk breaks b1,4 bonds between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetylglucosamine, a critical linkage in the peptidoglycans of bacterial cell walls [30]. In 1933, the nonlactose carbohydrate fraction of human milk was found to consist mainly of oligosaccharides [88]. In 1960, Montreuil and Mullet [89] determined that oligosaccharides constituted 2. Human milk contains a larger quantity of oligosaccharides than milk from other mammals, and its composition is singularly complex [90]. Only water, lactose, and lipids are present in greater amounts than oligosaccharides. Despite the fact that substantial energy must be expended by the mother to synthesize the many hundreds of different milk oligosaccharides, the infant does not use them as food. It is thought that they are present primarily to serve as receptor analogues that misdirect enteropathogen attachment factors away from gut epithelial carbohydrate receptors. Likewise, enteropathogens use the oligosaccharide portion of glycolipids and glycoproteins as targets for attachment of whole bacteria and toxins. Evidence is emerging that these glycoconjugates may have an important role in protection of the breast-fed infant from disease [64]. Lactadherin in human milk has been shown to bind rotavirus and to inhibit viral replication in vitro and in vivo [98]. A study of infants in Mexico showed that lactadherin in human milk protected infants from symptoms of rotavirus infection [87]. Free fatty acids and monoglyceride products of lingual and gastric lipase activity in human milk triglycerides may have antiviral and antiparasitic activity [30]. Human milk oligosaccharides also inhibit leukocyte endothelial adhesion and help explain the low rate of inflammatory disorders in breast-fed infants [98a]. The concept that this species might cause enteric disease was first suggested in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, when several veterinary workers described the association of diarrhea. In 1905, Moro [109] observed that Bacterium (now Escherichia) coli was found more often in the small intestines of children with diarrhea than in children without diarrhea. Adam [110,111] confirmed these findings and noted the similarity with Asiatic cholera and calf scours. Although Adam called these disease-producing organisms "dyspepsicoli" and introduced the important concept that E. Instead, these strains can be recognized only by identifying the enterotoxins or the genes encoding them. An autosomal dominant allele seems to be responsible for the specific intestinal receptor in piglets. Whether or not this epidemiologic pattern still prevails in impoverished countries is not well understood [149].
Staphylococcal species are Gram-positive antibiotics good or bad discount floxin 400mg without a prescription, non motile antibiotics zomboid generic 400 mg floxin with visa, catalase-positive antimicrobial wash generic 400mg floxin with mastercard, small virus medication generic floxin 200mg online, spherical bacteria (cocci), which, on microscopic examination, appear in pairs, short chains, or bunched in grape-like clusters. Many of the 32 species and subspecies in the genus Staphylococcus are potentially found in foods due to environmental, human, and animal contamination. Several staphylococcal species, including both coagulase-negative and coagulase-positive strains, have the ability to produce highly heatstable enterotoxins that cause gastroenteritis in humans. Staphylococcal enterotoxins can act as superantigens capable of stimulating an elevated percentage of T-cells. Staphylococci are atypical, in that they are able to grow at low levels of water activity, with growth demonstrated at aw as low as 0. They are resistant to proteolytic enzymes, such as trypsin and pepsin, which allows them to transit intact through the digestive tract. Illness Staphylococcal food poisoning (staphyloenterotoxicosis; staphyloenterotoxemia) is the name of the condition caused by the enterotoxins. Mortality: Death from staphylococcal food poisoning is uncommon, although it has occurred among the elderly, infants, and severely debilitated people. This level is indicative of unsanitary conditions in which the product can be rendered injurious to health. In highly sensitive people, ingestion of 100 to 200 ng of enterotoxin can cause symptoms. Onset: the onset of symptoms usually is rapid (1 to 7 hours) and in many cases acute, depending on individual susceptibility to the toxin, amount of toxin ingested, and general health. Illness / complications: Staphylococcal food poisoning generally causes self-limiting, acutely intense illness in most people. Symptoms: When ingested, the enterotoxin may rapidly produce symptoms, which commonly include nausea, abdominal cramping, vomiting, and diarrhea. In more severe cases, dehydration, headache, muscle cramping, and transient changes in blood pressure and pulse rate may occur. Duration: the illness is relatively mild and usually lasts from only a few hours to one day; however, in some instances, the illness is severe enough to require hospitalization. Pathway: Staphylococcal enterotoxins are stable in the gastrointestinal tract and indirectly stimulate the emetic reflex center by way of undetermined molecular events. It is thought that the vagus nerve is involved in the sequence of events that produce the emetic response. The true incidence is unknown for a number of reasons, including poor responses from victims during interviews with health officials; misdiagnosis of the illness, which may be symptomatically similar to other types of food poisoning (such as vomiting caused by Bacillus cereus emetic toxin); inadequate collection of samples for laboratory analyses; improper laboratory examination; and, most important, many victims do not seek medical attention because of the short duration of the illness. They can be found in the air, dust, sewage, water, milk, and food, or on food equipment, environmental surfaces, humans, and animals. Foods that require considerable handling during preparation and are kept slightly above proper refrigeration temperatures for an extended period after preparation are frequently involved in staphylococcal food poisoning. Unless heat processes are applied, staphylococci are expected to exist in any and all foods that are handled directly by humans or are of animal origin. Destruction of viable cells by heat does not destroy the biological activity of preformed staphylococcal enterotoxins. Staphylococci are present in the nasal passages and throats and on the hair and skin of 50% or more of healthy individuals. The incidence is even higher among those who associate with sick people and hospital environments. Contamination may be introduced into foods by direct contact with workers with hand or arm lesions caused by S. Food handlers are frequently the source of food contamination in staphylococcal outbreaks; however, equipment and environmental surfaces also can be sources. Avoiding time and temperature abuse of food products that are at high risk of containing S. Diagnosis Staphylococcal food poisoning is diagnosed based on isolation of the pre-formed enterotoxin or the isolation of enterotoxigenic staphylococci from the suspect food consumed and/or the vomitus or feces of the patient.
It is also important to use appropriate food composition tables with accurate nutrient values for the foods as consumed antibiotic questionnaire order 200 mg floxin with amex. First antimicrobial mouth rinse brands cheap floxin 200 mg with mastercard, the intake distribution must be adjusted to remove the effect of dayto-day variation of individual intake infection tooth extraction order line floxin. The statistical adjustments are based on assumptions about the day-to-day variation derived from repeat measurements of a representative subset of the group under study (Nusser et al infection prevention week 2014 order floxin on line. The resulting adjusted intake distribution narrows, giving a more precise estimate of the proportion of the group with usual intakes below the estimated requirements (Figure 8-2). The reason for this is the same as discussed earlier for individuals, namely that when the distribution of requirements for the chosen criterion is not known, the adequacy of an intake below a "recommended level" cannot be determined. This coincides with that put the probability of becoming hypertensive at some point in the future at over 90 percent for individuals 55 years of age (Vasan et al. A distribution of usual intakes, including intakes from supplements, is required to assess the proportion of the population that might be at risk of overconsumption. Likewise, an infant formula with a nutrient profile similar to human milk (after adjustment for differences in bioavailability) should supply adequate nutrients for an infant. In dietary survey data (Appendix Tables D-3 and F-1), water from food provided 19 percent of total water intake, or 0. A number of foods (especially fruits and vegetables) contain a substantial amount of water (moisture) (see Table 4-14). Unlike most other nutrients, intake of water is driven by need, as well as other factors. As discussed in Chapter 4, it is important to note that water requirements cannot be considered in isolation from macronutrient and electrolyte consumption because these nutrients are critical to water balance. The majority of body water is associated with fat-free mass (70 to 75 percent) in adults. Total body water averages approximately 60 percent of body weight with a range of 45 to 75 percent due primarily to differences in body composition. Diet composition, physical activity level, environmental exposure, pathophysiological factors. Potassium As described in detail in Chapter 5, potassium is the major intracellular cation and is required for normal cellular function. This level is based on an intake of naturally occurring potassium from dietary sources, primarily fruits and vegetables, which has been shown to be beneficial in reducing the adverse effects of sodium intake on blood pressure and possibly in reducing the risk of kidney stones. Bicarbonate or its precursors (organic anions typically associated with potassium in foods) may neutralize an excess acid load seen in typical Western-style diets, and may diminish bone turnover. Caution is warranted, however, in the consumption of potassium by individuals whose kidney function may be insufficient to excrete potassium adequately; in individuals taking medications known to decrease renal excretion of potassium. In assessing and planning for potassium intakes of individuals, important considerations that impact potassium requirements include the effects of environmental heat exposure and physical activity levels on potassium loss through sweat and the use of diuretics or other drug therapies commonly prescribed for the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure. These factors have the potential to influence potassium needs because they increase potassium losses in urine and sweat. Individuals who use diuretics should follow advice from their physician regarding potassium intake and the need for supplements since the type of diuretic used can affect whether appreciable amounts of potassium are lost in the urine. Once again, medical advice should be obtained, and use of potassium-containing salt substitutes should be undertaken only when advised by a physician. In planning diets for individuals and for groups, the dietary source of potassium is also important. Naturally occurring potassium is the cation found most abundantly in vegetable fruits. In contrast, the potassium added to foods or found in supplements is primarily in the form of potassium chloride. Potassium bicarbonate administration produces lower levels of calcium in urine compared with potassium chloride, suggesting that potassium bicarbonate or citrate are the forms most conducive to a reduced risk of renal stones. Because bicarbonate, but not chloride, can neutralize the acid generated from the metabolism of diets high in animal proteins, resulting in less bone turnover, potassium chloride also would not be expected to promote bone health as would be predicted with potassium bicarbonate. Sodium Chloride Sodium is the principle cation of the extracellular fluids and is the primary regulator of extracellular fluid volume and body water. Sodium and chloride are normally consumed together as sodium chloride (salt) in food. For this reason, Chapter 6 presents data on recommended intakes and effects of sodium as sodium chloride and assumes it applies to chloride unless otherwise noted. While the minimal amount of sodium required to replace insensible losses is estimated to be 0.
Discount floxin 400 mg without prescription. Rag Company Microfiber Upgrade.