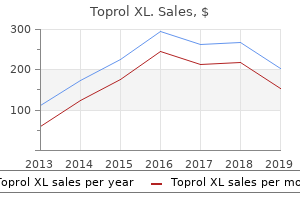
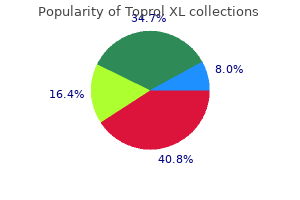
"Purchase generic toprol xl online, arteria iliaca externa".
By: G. Brontobb, MD
Medical Instructor, University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry
Scanning microscopy showed acid decreased the surface characteristics of non-root planed teeth heart attack quizlet generic toprol xl 50mg visa. Acid-etched root planed surfaces were flat with frequent depressions and numerous fiber-like structures arrhythmia nursing diagnosis buy 25mg toprol xl amex. Transmission microscopy revealed root planed and acid-etched surfaces produced a zone of demineralization of 4 um wide hypertension 150 100 25mg toprol xl for sale. When these surfaces were treated by citric acid (pH 1 for 3 minutes) this smear layer was removed arrhythmia heart murmur toprol xl 100mg low price. The result was a fibrous matlike structure with a fibrillar texture having numerous funnel-shaped depressions corresponding to open dentinal tubules. They examined the dentinal surfaces for root roughness and maximal exposure of the collagen surface. The burnished specimens were found to have patent dentinal tubules and an intertubular area with a very distinct "shag carpet" appearance of deeply tufted collagen fibrils. The passively placed citric acid specimen exhibited open dentinal tubules with a matted collagen surface. They proposed that the burnishing application removed more inorganic material through a combined mechanical/chemical process while fluffing and separating the entangled fixed dentin collagen. They showed that acid-treated teeth had a fibrillar zone 3 to 8 um thick consisting of collagenous fibrils of the dentin exposed during acid treatment. There appeared to be a layer of cells in dynamic activity and distinct attachment to dentin with cells migrating over the root surface. In the controls, there were large areas devoid of cells and other connective tissue components. This suggests that citric acid treatment may result in fibrin clot stabilization and initiate wound healing that results in new connective tissue attachment. They found that: 1) root planing improves diseased roots and that root planing followed by citric acid demineralization improves diseased roots to a level comparable to non-diseased roots; 2) citric acid demineralization alone improves diseased roots to a level comparable to root planed diseased roots; and 3) acid demineralization results in both collagen fiber exposure and a more hospitable environment. They found that passive applications for 5 minutes and burnished applications for 3 minutes both produced seemingly optimal surface characteristics consisting of a fine, fibrillar network of exposed collagen and a reduced or eliminated smear layer. Citric acid pH 1 was applied to dentin surfaces prepared from extracted teeth by 1) immersion; 2) placement of saturated cotton pellets; 3) burnishing with cotton pellets; or 4) camel hair brush. Immersion demonstrated tufting of intertubular dentin fibrils and wide open dentinal orifices. Pellet placement revealed a more matted surface and some debris inside the orifices. Two of 8 slabs showed tufting with widened tubular openings, while 6 of 8 showed surface smearing with complete obturation of the tubules. The camel hair brush resulted in surface characteristics close to those treated by immersion (tufting with widened tubules). Immersion resulted in the greatest number of openings followed by cotton pellet placement and camel hair brush. The measurements of calcium parts per million released for citric acid concentrations of 0, 10, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, and 65% were determined at 1, 2, and 3 minutes. Denuded root surfaces healed with cementogenesis with a secure fiber attachment at 6 weeks. However, circumferential and bifurcation defects only healed with approximately 10% reattachment. Through and through furcation defects were created and allowed to accumulate plaque for 42 days. Thirteen of 23 acidtreated furcations demonstrated complete new attachment; 8 were incomplete and 2 remained patent. Poison and Proye (1982) also studied the effects of citric acid conditioning in the monkey. Twelve teeth in 4 monkeys were extracted and the coronal third was planed to remove the fibers and cementum. The root surfaces were then treated with citric acid for 3 minutes and then re-implanted into their sockets. At days 1 and 3, a fibrin linkage was shown between the periodontal ligament and the root surface. A new connective tissue attachment was present at 21 days with no cementum formation. Ultrasonics and Air Abrasives this led Poison and Proye (1983) to determine the healing sequence related to the fibrin clot and its interaction with collagen.
The cuff induces an inflammatory response that results in the growth of fibrous tissue that anchors the catheter in place arrhythmia books buy cheap toprol xl. These catheters are used for drug and fluid administration heart attack heartburn toprol xl 50mg otc, antibiotic therapy pulse pressure variation values generic 25mg toprol xl visa, chemotherapy heart attack blood test purchase toprol xl 25mg without prescription, nutritional therapy, hemodialysis, and bone marrow transplantation. These catheters are more comfortable and discreet for the patient than nontunneled catheters, but they require a minimally invasive surgical procedure that carries with it attendant risks, such as hemorrhage, pneumothorax, and infection. Implantable ports, such as portacaths, are surgically placed completely under the skin, usually as a central subclavian port in the subcutaneous pocket of the upper chest wall. These are useful for long-term or permanent vascular access and carry with them a lower infection risk, as they are not external to the body. The port, which is made of plastic, titanium, or stainless steel, is a hollow reservoir with a silicone septum and an outlet that connects to a polyurethane or silicone catheter that enters one of the central veins. To administer treatment, a Huber needle is used to puncture the skin and the septum over the reservoir. These ports can be punctured up to 2,000 times and have been reported to be in place for several years. The catheter is then advanced to the distal superior vena cava/proximal right atrium. Umbilical venous access is most often used for fluid and medication administration, blood sampling, and measurement of central venous pressure; umbilical artery access may be used to monitor arterial pressure or blood gases and to administer fluids and medications. A more in-depth discussion regarding education and training and their roles in patient safety initiatives can be found in Chapter 4. Rarely, contamination of the infusate (such as parenteral fluid, intravenous medications, or blood products) can be the source of infection. Infusate can become contaminated during the manufacturing process (intrinsic contamination) or during its preparation or administration in the patient care setting (extrinsic contamination). Other catheters and their construction materials contribute to the formation of fibrin sheaths, which is why silastic catheters have a higher risk of infection associated with their use than do polyurethane catheters. Finally, some catheters are more thrombogenic (tend to produce blood clots) than others, which may predispose them to colonization and infection. Resistance to third-generation cephalosporins has increased significantly among E. After the catheter is inserted into the bloodstream, plasma proteins begin to adhere to it, which can result in the formation of a fibrin sheath around the catheter. Dispersal of single-cell microorganisms or clumps from the biofilm results in hematogenous dissemination of biofilm bacteria. A focus on proper catheter maintenance is important in minimizing infections that occur with longer dwell times (associated with the intraluminal route of contamination). In neonates, bloodstream infections are classified as early onset (within 72 hours of birth) or late onset (more than 72 hours after birth)7,49,50: Early-onset bloodstream infections (non-devicerelated) are acquired in the birth canal and are often multisystem in nature, with high mortality rates. Risk factors associated with early-onset sepsis include prolonged rupture of membranes, prematurity and low birth weight, maternal fever, and chorioamnionitis. Risk factors for late-onset bloodstream infections include low birth weight and parenteral nutrition therapy. The catheter material can also influence the development of bloodstream infection. Peripherally inserted central venous catheters are not superior to central venous catheters in the acute care of surgical patients on the ward. Risk of catheter-related bloodstream infection with peripherally inserted central venous catheters used in hospitalized patients. Central Access: Umbilical Artery & Vein Cannulation: Clinical Best Practice Guideline. Mollee P, Jones M, Stackelroth J, van Kuilenburg R, Joubert W, Faoagali J, Looke D, Harper J, Clements A. Catheter-associated bloodstream infection incidence and risk factors in adults with cancer: A prospective cohort study.
25mg toprol xl with mastercard. #1🥇 High Blood pressure Types-உயர் இரத்த அழுத்தம் இருப்பதை உறுதி செய்வது எப்படி?Tamil Dr MOHANAVEL.
There is little doubt the fibroblast plays an important role in the pathogenesis of this condition; however blood pressure medication with hydrochlorothiazide order cheap toprol xl line, individual patient sensitivity to the drug or its metabolites 01 heart attackm4a discount 25mg toprol xl free shipping, plasma concentrations of the drug zopiclone arrhythmia buy 50 mg toprol xl fast delivery, dental plaque scores blood pressure ranges by age and gender toprol xl 100 mg with amex, and gingivitis have all been proposed as important contributing factors (Wysocki et al. Although Seymour and Smith (1991) reported that plaque control measures alone did not prevent gingival overgrowth in cyclosporin-treated adult renal transplant patients, Hancock and Swan (1992) provided clinical evidence in a case report that plaque control without drug withdrawal or surgical excision can be successful in significantly reducing established nifedipine-induced gingival overgrowth. Renal transplant patients medicated with a combination of cyclosporin and nifedipine have a significantly higher gingival overgrowth score (P = 0. Nifedipine is a calcium channel blocking agent used in the treatment of vasospastic angina, chronic stable angina, and ventricular arrhythmias. Its principal action is to inhibit the influx of extracellular calcium ions across cardiac and vascular smooth muscle cell membranes, without changing serum calcium concentration. This prevents the contractile processes of cardiac and vascular smooth muscle from occurring, resulting in a dilatation of the main coronary and systemic arteries. The incidence of gingival overgrowth in response to nifedipine, and the role of drug dosage and duration are presently speculative (Butler et al. Clinically, nifedipine-induced gingival overgrowth closely resembles phenytoin enlargement. Both exhibited increased extracellular ground substance as well as increased numbers of fibroblasts. In addition, fibroblasts with numerous, large cytoplasmic structures resembling secretory granules were the striking electron microscopic finding in specimens examined. Because the authors believed that these granules represented newly synthesized ground substance prior to extrusion from the fibroblast, they concluded that an increase in ground substance is the primary cause of overgrowth in these conditions. The authors reported that 38% of the patients taking nifedipine, 21% of the patients taking diltiazem, and 19% of the patients receiving verapamil had gingival enlargement, compared with only 4% among controls. The blood vessels were not stained but the adjacent areas demonstrated intense fluorescence with these antibodies. In contrast to these, fibronectin localized with a varied intensity in the different areas of the tissue and presented a "cloud-like" structure. This study suggests differences between the matrix components in nifedipine-induced hyperplasia and confirms the heterogeneity of the matrix in health and in gingival alterations. They noted marked gingival overgrowth in the molar regions, regardless of gingival infection although the latter increased the degree of enlargement. Treatment of Drug-Induced Gingival Hyperplasia the best treatment of drug-induced gingival enlargement is discontinuing use of the associated drug. The enlargement will slowly become smaller and disappear in a matter of weeks to months. Therefore, prevention of secondary inflammation and surgical treatment of the enlargement become the only realistic choices (Carranza, 1990). Treatment of drug-induced gingival overgrowth is based upon the severity of overgrowth and the ultimate goals of therapy. Both non-surgical and surgical approaches to treatment have been used successfully. Non-surgical therapy consisting of thorough scaling and root planing plus improvement in oral hygiene is the primary method of treating the inflammatory component of gingival overgrowth. Adjunctive therapy such as the daily use of chlorhexidine gluconate mouthrinses may also be considered. Although dramatic results can be obtained using non-surgical treatment alone, some lesions will not respond adequately and require surgical intervention. Surgical approaches to gingival overgrowth are gingivectomy and the flap technique. Gingivectomy is simple and facilitates maintenance care, but it creates an open wound and potential for post-operative complications (Carranza, 1990). The flap technique thins gingival tissues internally and repositions them apically without significantly removing or altering the external surface of the gingiva (Carranza, 1990). This technique facilitates wound closure and maintenance care, and reduces potential for post-operative complications.
Again blood pressure chart of human body cost of toprol xl, the one-compartment model assumes that the drug is distributed to tissues very rapidly after intravenous administration arteriovenous graft purchase toprol xl 25mg overnight delivery. Compartmental model representing transfer of drug to and from central and peripheral compartments blood pressure yahoo answers purchase toprol xl 25mg on line. The two-compartment model can be represented as in Figure 1-18 blood pressure medication od order toprol xl 50mg fast delivery, where: X0 = dose of drug X1 = amount of drug in central compartment X2 = amount of drug in peripheral compartment K = elimination rate constant of drug from central compartment to outside the body K12 = elimination rate constant of drug from central compartment to peripheral compartment K21 = elimination rate constant of drug from peripheral compartment to central compartment drug in tissue and plasma, plasma concentrations decline less rapidly (Figure 1-19). The plasma would be the central compartment, and muscle tissue would be the peripheral compartment. Volume of Distribution Until now, we have spoken of the amount of drug (X) in a compartment. After an intravenous dose is administered, plasma concentrations rise and then rapidly decline as drug distributes out of plasma and into muscle tissue. Volume of distribution (V) is an important indicator of the extent of drug distribution into body fluids and tissues. V relates the amount of drug in the body (X) to the measured concentration in the plasma (C). Thus, V is the volume required to account for all of the drug in the body if the concentrations in all tissues are the same as the plasma concentration: volume of distribution = amount of drug concentration the body is primarily composed of water. To calculate the volume of the tank, we can place a known quantity of substance into it and then measure its concentration in the fluid (Figure 1-20). Conversely, a small volume of distribution often indicates limited drug distribution. Volume of distribution indicates the extent of distribution but not the tissues or fluids into which the drug distributes. Two drugs can have the same volume of distribution, but one may distribute primarily into muscle tissues, whereas the other may concentrate in adipose tissues. Approximate volumes of distribution for some commonly used drugs are shown in Table 1-2. When V is many times the volume of the body, the drug concentrations in some tissues should be much greater than those in plasma. To illustrate the concept of volume of distribution, let us first imagine the body as a tank filled with fluid, as X = amount of drug in body V = volume of distribution C = concentration in the plasma As with other pharmacokinetic parameters, volume of distribution can vary considerably from one person to another because of differences in physiology or disease states. The volume of a tank can be determined from the amount of substance added and the resulting concentration. Drug elimination complicates the determination of the "volume" of the body from drug concentrations. In this example, important assumptions have been made: that instantaneous distribution occurs and that it occurs equally throughout the tank. This example is analogous to a one-compartment model of the body after intravenous bolus administration. However, there is one complicating factor-during the entire time that the drug is in the body, elimination is taking place. So, if we consider the body as a tank with an open outlet valve, the concentration used to calculate the volume of the tank would be constantly changing (Figure 1-21). If we give a known dose of a drug and determine the concentration of that drug achieved in the plasma, we can calculate a volume of distribution. However, the concentration used for this estimation must take into account changes resulting from drug elimination, as discussed in Lessons 3 and 9. Examples include digoxin, diltiazem, imipramine, labetalol, metoprolol, meperidine, and nortriptyline. Note that this plot is a curve and that the plasma concentration is highest just after the dose is administered, at time zero (t0). Because of cost limitations and patient convenience in clinical situations, only a small number of plasma samples can usually be obtained for measuring drug concentrations (Figure 1-24). From these known values, we are able to predict the plasma drug concentrations for the times when we have no samples (Figure 1-25). With a simple one-compartment, intravenous bolus model, a plot of the natural log of plasma concentration versus time results in a straight line. The prediction of drug concentrations based on known concentrations can be subject to multiple sources of error. However, if we realize the assumptions used to make the predictions, some errors can be avoided. From a mathematical standpoint, the prediction of plasma concentrations is easier if we know that the concentrations are all on a straight line rather than a curve.