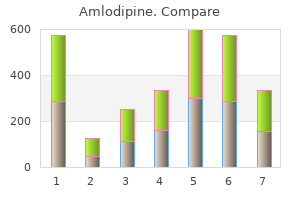
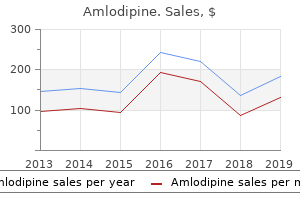
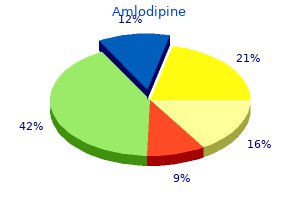
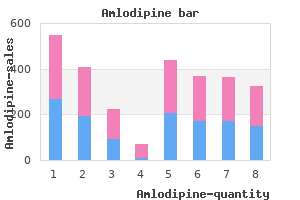
"5mg amlodipine visa, blood pressure watches".
By: P. Osko, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Co-Director, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
Clinical signs of the compensatory phase can be difficult to identify but may include tachycardia arteria del corazon cheap amlodipine 5 mg otc, injected mucous membranes with a rapid capillary refill time blood pressure 5020 buy generic amlodipine online, and bounding pulses arrhythmia blood pressure order amlodipine 10mg line, while blood pressure ranges from normal to slight hypertension halou arrhythmia order genuine amlodipine on line. Cats do not usually display this response unless they are in tremendous pain (Kirby 2008). If the loss is too great for them to restore normal function or is persistent for prolonged periods of time, the early decompensatory stage of shock begins (Kirby 2008). Reserves are beginning to diminish, and the cytokines from hypoxic tissues are now entering the systemic circulation. Clinical signs of this phase include tachycardia, weak pulses, hypotension, pale mucous membranes, prolonged capillary refill time, hypothermia, and normal to decreased mentation. This is where aggressive volume resuscitation is essential to decrease mortality (Kirby 2008). The late decompensatory phase is the final and terminal stage of all forms of shock. Anaerobic metabolism is nearly 20 times less productive than aerobic metabolism, and, if continued, this phase progresses to circulatory collapse and insufficient blood flow to the brain and heart. Since the heart cannot sustain any kind of compensatory response at this late phase, the animal rapidly declines and dies. Clinical signs for this phase include bradycardia, severe hypotension, pale to cyanotic mucous membranes, undetectable capillary refill time, weak to absent pulses, hypothermia, and decreased to comatose mentation. The goal of shock therapy specifically is to meet oxygen delivery requirements to tissues and to shut off the neuroendocrine response as quickly as possible. In cases of hypovolemic, obstructive, and distributive shock, therapy is initiated with fluid administration and supplemental oxygen (Davis 2008). Concurrently, laboratory samples are obtained, and pain management is provided for any animal experiencing pain. Patients presenting with any type of hemorrhage should also have their bleeding slowed or stopped to minimize ongoing hypovolemia. Open lacerations should have pressure bandages applied as soon as possible, and abdominal hemorrhage can be slowed by placing a wrap around the abdomen. Patients suspected of having sepsis should be started on antibiotic therapy ideally within 1 hour of presentation. Later, following intravenous fluid therapy and oxygen administration, fractures must be addressed as part of initial stabilization. Open fractures should be flushed and bandaged to stabilize the fracture and protect the wound from further contamination. Intravenous Catheter Placement the intravenous catheter is the direct line from veterinary paraprofessional to the patient. It allows for rapid fluid administration, and necessary medications can be given with immediate effects. One of the few exceptions to placing an intravenous catheter first upon patient arrival is when the patient is in severe cardiac or respiratory distress and any stress may push them into respiratory or cardiac arrest. Therefore, some patients require an initial hands-off minimalistic approach, oxygen therapy, possible sedation or thoracocentesis, and catheterization later. Severely compromised patients will present more difficulty in catheter placement because not only is the vein difficult, if not impossible, to visualize, but hypotension can prevent blood from appearing in the hub of the catheter when the vein is entered (flash). Further discussion on intravenous catheters and venous access is available in Chapter 3, "Venous Access. InitialPatientManagement 31 Physiology Fluid in the body is either in a cell (intracellular) or outside of a cell (extracellular). The three major fluid compartments are the intracellular, intravascular, and interstitial spaces. Fluid movement from the intravascular to interstitial and intracellular compartments occurs at the capillary membrane, and this membrane is freely permeable to water and small molecular weight particles. The intracellular compartment is separated from the interstitial compartment by a cell membrane, which is freely permeable to water but not small or large molecular weight particles. Fluids to be administered must concentrate within the compartment where the volume deficit lies. Colloids are often used for intravascular volume replacement, while crystalloids help with intravascular and interstitial volume replacement. However, it is important to understand that the majority of crystalloids do not remain in the intravascular space beyond an hour.
In cases of severe metabolic acidosis blood pressure chart enter numbers buy amlodipine 5mg fast delivery, the patient may exhibit Kussmaul respiration (slow deep breathing pattern) arrhythmia ablation is a treatment for buy generic amlodipine online. These patients often have an acute onset of abdominal pain and may also have abdominal distension hypertension categories generic amlodipine 2.5 mg visa, especially if concurrent pancreatitis or peritonitis is present hypertension 2008 buy amlodipine cheap online. Cats may exhibit diabetic neuropathy with plantigrade posture (hocks touch the ground when the cat walks-due to sciatic neuropathy). Leukocytosis can be attributed to infection (demonstrated by left shift/toxic changes in neutrophils) or inflammation. Biochemical panels can often demonstrate liver abnormalities caused by hepatic lipidosis, pancreatitis, or extrahepatic biliary obstruction due to severe pancreatitis. Primary renal failure can occur due to hypoperfusion of the kidney as a result of hypovolemia. Hyperlipidemia is often noted due to the increase in triglycerides, cholesterol, lipoproteins, chylomicrons, and free fatty acids. In humans, this contributes to atherosclerotic vascular disease and coronary artery disease. Pancreatic enzymes (amylase and lipase) are often elevated due to concurrent chronic or acute pancreatitis, chronic inflammation, or renal failure. If renal failure or insufficiency is present, amylase and lipase may be elevated due to decreased renal excretion. Urinalysis will often reveal glucosuria, ketonuria, proteinuria, bacteriuria, with or without significant pyuria and hematuria. Urine strips do not detect -hydroxybutyrate, but ketoacidosis cannot occur without this acid. Adding a drop or two of hydrogen peroxide to a urine sample that has tested negative for ketones may convert this ketoacid to acetoacetate and acetone, which are detectable on the urine strip. An abstract in the Journal of Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care (March 2003, 13[1]) compared plasma ketones with urine ketones, and this practice was found to be clinically useful for confirming ketosis. Even if the initial serum levels of sodium, potassium, phosphorous, and magnesium are normal, there is frequently a whole body depletion of these ions from hyperglycemic diuresis. Abnormalities are often diagnosed during treatment, when electrolyte shifting between the intracellular and extracellular spaces can reveal an overall depletion of one or all of these electrolytes. The slower the recovery process, the better the probability of successful long-term treatment of the patient. Goals of treatment are to restore and maintain adequate fluid balance and effective circulating volume, provide sufficient amounts of insulin to normalize glucose metabolism, to correct acidosis and electrolyte abnormalities, and to treat any and all underlying or predisposing causes. Strict aseptic technique should be used during all treatments of diabetic patients due to their increased susceptibility to bacterial infection. Proper catheter care of a central line and monitoring is vital to prevent secondary infection. If the patient is not urinating regularly, it is best to place a urinary catheter with a closed collection system in order to ensure adequate urine production, especially in azotemic patients. The concentration of diabetogenic hormones is also reduced with fluid administration. It is important to note that, unlike glucose levels, ketone bodies do not decrease with fluid administration alone. If sodium is >140 mmol/L, then the fluids should be changed to a buffered solution containing less sodium than 0. In patients with severe acidosis, and/or with mild hyponatremia, an isotonic buffered solution, such as Normosol-R, may be the best choice. Hypotonic solutions should be used with caution, if at all, due to the potential of excessive free water administration contributing to cerebral edema, and even death. However, since the hyperosmolality is mostly due to hyperglycemia and hypernatremia, and because it typically developed over a prolonged period of time, usually judicious administration of balanced isotonic fluids will lead to the quickest resolution of hyperosmolality. The fluid rate is dependent on the degree of dehydration, the presence of shock or hypovolemia, and ongoing losses. Boluses should be started incrementally at 20 mL/kg and repeated to effect (Mathews 2006).
These results suggest a possible synergism in affecting neurological dysfunction and development hypertension xerostomia buy genuine amlodipine on line, but no in vivo demonstration of such a synergism is available hypertension 6 year old buy 10mg amlodipine overnight delivery. Survival of male offspring in all Kanechlor groups showed a marked decline blood pressure pictures buy generic amlodipine on-line, compared with controls blood pressure over 180 amlodipine 5mg otc, at about 5 weeks after birth; at 10 weeks after birth, male offspring survival percentages were about 60, 60, and 40% for the groups with Kanechlor plus 0, 0. In a study of minks, reproductive end points, serum thyroid hormone levels (T3 and T4), and histology of brain, kidney, adrenals, pituitary, and thyroid were evaluated in groups of adult ranch-bred minks fed a commercial mink food supplemented with 0 or 1 ppm Aroclor 1254, 1 ppm Hg as methylmercury, 1 ppm Aroclor 1254 + 1 ppm methylmercury, or 0. Exposed groups contained 12 females and 4 males; control groups had 15 females and 5 males. During the third month of exposure, eight females and one male in the 1 ppm methylmercury group, and three females in the 1 ppm Aroclor + 1 ppm methylmercury group, died, displaying convulsions, tremors, and lethargy. The mortality was attributed to a combination of cold stress and methylmercury poisoning, and surviving minks were fed diets containing 1 ppm methylmercury every other day for the remainder of the study. No exposure-related effects were found on the thyroid, pituitary, adrenal glands, or serum T4 or T3 levels in adult minks that survived the 8-month exposure period. The average number of offspring per female at weaning (5 weeks after birth) was significantly (p< 0. An alternative interpretation of the results is that combined exposure induced postnatal mortality at concentrations of the individual agents (1 ppm) that did not induce postnatal mortality, but it is not possible to discern if they acted together in a less-than-additive, additive, or greater-than-additive manner without including treatments involving 2 ppm concentrations of the individual agents alone. A clear demonstration of synergistic action would have involved increased postnatal mortality produced by the 0. Intermediate-duration exposures of quail to methylmercury or Aroclor 1260 in the diet led to accumulation of porphyrins in liver; hepatic porphyrin levels in quail exposed to both agents simultaneously were similar to levels predicted based on additivity of response (Leonzio 1996b). The individual agents, at the concentrations used in this mixture, did not inhibit the in vitro binding of 17-estradiol to the estrogen receptors, with the exception that 2. Combined exposure reduced total egg production over the study period by about 35% compared with controls. About 25% of the decline in egg production in the combined exposure group was attributed to egg eating. Simultaneous exposure of rats to Aroclor 1254 or 1260 and chemicals of environmental concern such as the pesticides mirex, photomirex, and/or kepone in the diet resulted in increased severity of the liver lesions attributed to exposure to chlorinated biphenyls alone (Chu et al. A single dose of iron dextran in mice fed Aroclor resulted in a significant increase in octoploid nuclei within 2 weeks; it persisted for 6 months and resulted in massive hepatic porphyria. This detoxification might occur if the epoxide of 1,1-dichloroethylene isomerizes rapidly to an aldehyde before reacting with tissues. Co-administration of cadmium and Aroclor 1248 resulted in a significant increase in growth retardation and plasma cholesterol, compared to controls or rats fed a diet containing cadmium or Aroclor 1248 alone. This resulted in an increased formation and excretion of mutagenic metabolites in the urine. Intraperitoneal injection of Aroclor 1254 to mice on Gd 19 protected the offspring from lung tumors, but increased the incidence of liver tumors, following injection of N-nitrosodimethylamine on postnatal day 4 or 14 (Anderson et al. Reasons may include genetic makeup, age, health and nutritional status, and exposure to other toxic substances. Data from animal studies suggest that the rate of absorption following oral exposure is greater than that following inhalation or dermal exposures. In addition, emesis may result in aspiration of the lipid materials into the lungs, possibly causing lipoid pneumonitis. Repetitive administration of activated charcoal might be useful in preventing reabsorption of metabolites. For the general population, especially subgroups that consume diets high in contaminated fish. Some of the toxic effects, such as immunological effects, body weight loss, enzyme induction and porphyria, appear to be mediated by a common initial mechanism involving the Ah cytosolic receptor (Poland et al. Clinical intervention to interfere with Ah-receptor independent mechanisms have not been developed. The purpose of this figure is to illustrate the existing information concerning the health effects of polychlorinated biphenyls. The relative contribution of the inhalation and dermal routes in the occupational exposures is unknown, but existing information on health effects in exposed workers is included with inhalation exposure in Figure 3-5.
Hepatogenous photosensitization of sheep in California associated with ingestion of Tribulus terrestris (puncture vine) J Vet Diagn Invest heart attack jeff x ben generic amlodipine 2.5 mg free shipping. Laboratory Results: Three-view radiographs of the thorax revealed a soft tissue opacity in the left 1-1 blood pressure in the morning buy amlodipine with mastercard. An infiltrative neoplasm is present throughout the globe arrhythmia is another term for buy cheap amlodipine on line, markedly expanding the iris (black arrows) sinus arrhythmia buy 10mg amlodipine with amex, elevating the choroid and retina at the back of the globe, and extending through the sclera into the surrounding soft tissue (green arrows). Eye, cat: Closer view of the iris, which is expanded by an infiltrative epithelial neoplasm which forms variably sized tubules and acini, lined by papillary projections of neoplastic cells. Additionally, aggregates of neoplastic cells extend through the sclera into the episcleral stroma, with evidence of vascular invasion and, in the dependent portion, focal scleral thinning (staphyloma) and prominent regionally extensive periscleral desmoplastic spindle cell proliferation. Moderate numbers of lymphocytes and plasma cells are multifocally present within the uveal tract 1-3. Eye, cat: the retina (right) is detached and the anterior surface is lined by neoplastic cells. The amongst the neoplastic underlying choroid (center) is lifted off the connective tissue by a lining of neoplastic cells forming population. There is mild which appears to be associated with the left cupping of the optic nerve head with mild gliosis caudal lobar bronchus. The lens (not present in the submitted Histopathologic Description: the slides sections) exhibits extensive subcortical submitted to the conference contain the vertical cataractous change, characterized by eosinophilic section of a feline globe, which was collapsed as spherical globules (Morgagnian globules) and the result of a reported posterior rupture during migration of the epithelium along the posterior enucleation. Within sections of eyelid (not infiltration of the choroid and anterior uvea by a submitted), moderate numbers of lymphocytes neoplastic population of epithelial cells causing and plasma cells infiltrate the subepithelial extensive retinal detachment and complete stroma. Cells have indistinct cell borders and retinal detachment and atrophy, multifocal uveitis, moderate to ample amount of eosinophilic and cataractous change. Vascular attenuation with areas of lumen occlusion, serous exudation, and retinal hemorrhage in the peripapillary retina are also common. The pathogenesis of the ophthalmoscopic lesions is thought to be neoplastic embolization of branches of the short posterior ciliary arteries, which supply retinal and choroidal circulation. Eye, cat: Within the extraocular soft tissues, nests of neoplastic cells are surrounded by a prominent desmoplastic response. Growth of the indicator, with cats with moderately differentiated metastatic lesions along the vascular endothelium primary lung tumors having reportedly a leads to segmental loss of perfusion and significantly longer survival time (median 698 subsequent necrosis of the overlying retina and days) than cats with poorly differentiated primary choroid. Intraocular metastasis may be caudal lung, the most commonly affected lung underestimated since ophthalmoscopic and field by primary lung tumors in cats. Other sites of follow-up with the oncology team was metastasis of primary lung tumors in cats include recommended. The owners declined any further skeletal muscle, and multiple thoracic and workup, however. Conference Comment: this is an excellent descriptive slide with extensive ocular changes. Conference participants agreed the neoplasm is likely the result of metastasis from the pulmonary mass identified clinically. In the cat, lymphoma is by far the most prevalent metastatic tumor in the eye, although virtually any malignant neoplasm can localize within the uveal tract. Among primary ocular tumors, melanoma, lymphoma, posttraumatic sarcoma and iridociliary adenocarcinoma are most common in cats. Iridociliary adenocarcinoma is a reasonable differential in this case, but these typically benign neoplasms tend to infiltrate and expand the posterior chamber, often in solid sheets, in contrast to this case which filed along the uvea and choroid forming tubules. A round cell variant resembling lymphoma and osteo- or chondrosarcoma also occur following lens trauma, albeit at a much lower frequency. Feline lung-digit syndrome: unusual metastatic patterns of primary lung tumours in cats. Prognosis factors for survival in cats after removal of a primary lung tumor: 21 cases (1979-1994). The owners had not seen the cat drinking or using the litter box for the past few days. He did have access to a screened porch and was on Frontline but no heartworm preventative. The next morning the cat was still dull and dysphoric and soon developed cardiac and respiratory arrest.
Purchase amlodipine 5 mg with visa. Does alcohol cause high blood pressure?.
There was a significant amount of serosanguineous fluid in the trachea and large bronchi blood pressure levels.xls buy 5mg amlodipine fast delivery. There was a moderate amount of dark red to black fecal material in the large intestine blood pressure medication side effects discount amlodipine 10 mg with amex. Histopathologic Description: Blood vessels throughout the lung arrhythmia graphs purchase amlodipine online from canada, liver blood pressure lab report buy amlodipine 2.5mg fast delivery, pancreas, adrenal glands, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract are partially to almost completely occluded by few to numerous macrophages containing protozoal schizonts consistent with Cytauxzoon felis. Similar organisms are within macrophages filling subcapsular, cortical, and medullary sinuses of lymph nodes as well as within the splenic red pulp. Lung, cat: At subgross examination, while pulmonary vasculature is prominent, blood is not evident within larger vessels. Lung, cat: Alveolar septa are expanded up to 3x normal by numerous macrophages, dilated capillaries, edema, and fibrin. The adjacent pulmonary venule is expanded and almost occluded by the present of numerous macrophages enlarged by schizonts of Cytauxzoon felis. Bobcats and possibly other wild felids are believed to serve as the reservoir host. Clinical findings include acute illness with fever, depression, anorexia, pallor, icterus, and usually death within a few days. The urine in the early hemolytic phase is highly concentrated, acidic and contains large amounts of protein, bile and blood. This more sensitive method of detection has lead to the identification of cats that either have subclinical infection or that have recovered from an infection and become chronic carriers. Lymph node: Lymphadenitis, histiocytic, diffuse, mild, with lymphoid depletion, hemorrhage, thrombosis, and numerous intravascular intrahistiocytic schizonts. Lung: Pneumonia, interstitial, histiocytic, diffuse, mild, with numerous intravascular intrahistiocytic schizonts. Conference Comment: Two different slides were distributed for this case, both exhibiting numerous intravascular apicomplexans typical of Cytauxzoon felis. The schizonts within circulating macrophages demonstrated in this case are first cycle of schizogony, and in chronic disease, cytomeres are released and infect erythrocytes during the second cycle of schizogony to form the piroplasm ring (signet ring) often evident on cytology. Ischemic damage can also cause cerebral necrosis, appearing similar in some respects to feline ischemic encephalopathy and thiamine deficiency. Genetic variability of Cytauxzoon felis from 88 infected domestic cats in Arkansas and Georgia. Detection of persistent Cytauxzoon felis infection by polymerase chain reaction in three asymptomatic d o m e s t i c c a t s. Histopathologic Description: Stomach: Expanding the submucosa and elevating the overlying gastric mucosa there is a mostly well demarcated, but unencapsulated, densely cellular and partially infiltrative growing ovoid mass of up to 1. The cells are closely packed in sheets with a moderate amount of fibrovascular stroma. The chromatin is finely stippled, in some nuclei finely clumped with a distinct round centrally located eosinophilic nucleolus in each nucleus. Preexisting vessels within the mass are thickened by increased numbers of spindle cells in the media (media hyperplasia) and deposition of extracellular, eosinophilic, fibrillar material (collagen). Additionally, throughout the mass multifocal acute hemorrhages with extravasation of erythrocytes and fibrin, depositions of granular golden-brown pigment (hemosiderin) in macrophages and multiple areas of necrosis are present. Submucosal tissue surrounding the neoplasm is expanded by edema, occasional hemorrhages, multiple hemosiderin-laden macrophages and moderate numbers of plasma cells. Stomach, dog: Within the pyloric submucosa, there is an expansile, well-demarcated, densely cellular neoplasm. Stomach, dog: the neoplasm is composed of uninucleated and multinucleate plasma cells. Stomach, dog: Multifocally, neoplastic plasma cells are separated by homogenous to fibrillar eosinophilic material (presumed amyloid) which is occasionally engulfed by multinucleated foreign-body type macrophages.