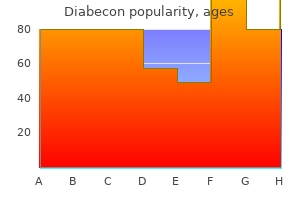
"Order 60caps diabecon free shipping, diabetes mellitus type 2 nice".
By: X. Jesper, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine at Arkansas State University
Normally blood sugar diabetes generic 60caps diabecon with mastercard, the lower part of the right ventricle abuts the sternum and air-filled lung extends down between the sternum and the right ventricle and pulmonary artery diabetes insipidus zwanger purchase diabecon 60 caps visa. When the retrosternal space is obliterated by cardiac density kidney stones diabetes type 2 discount 60caps diabecon overnight delivery, right ventricular enlargement is present blood sugar issues symptoms 60 caps diabecon for sale. Both the electrocardiogram and the chest X-ray may be used to assess cardiac chamber size. Left atrial enlargement is best detected by chest X-ray, whereas ventricular or right atrial enlargement is detected better by an electrocardiogram. Cardiac contour In addition to the search for information about cardiac size on the posteroanterior view of the heart, the practitioner should direct attention to distinctive cardiac contours, such as the boot-shaped heart of tetralogy of Fallot. In conditions with right ventricular hypertrophy, the cardiac apex may be turned upwards, whereas conditions with left ventricular hypertrophy or dilation lead to displacement of the cardiac apex outwards and downward towards the diaphragm. In infants with a prominent thymus, the aortic knob is usually obscured, and normal aortic arch position is inferred from the rightward displacement of the trachea in a properly positioned posteroanterior chest film. A right aortic arch is common in tetralogy of Fallot and truncus arteriosus and can be diagnosed by leftward displacement of the trachea. Pulmonary vasculature the status of the pulmonary vasculature is the most important diagnostic information derived from the chest X-ray; this function has not been replaced by the 1 Tools to diagnose cardiac conditions in children 53 echocardiogram. The radiographic appearance of the blood vessels in the lungs reflects the degree of pulmonary blood flow. Because many cardiac anomalies alter pulmonary blood flow, proper interpretation of pulmonary vascular markings is diagnostically helpful. It is one of the two major features discussed in this book for initiating the differential diagnosis. The lung fields are assessed to determine if the vascularity is increased, normal, or diminished, reflecting augmented, normal, or decreased pulmonary blood flow, respectively. As a check of the logic of interpretation, the vascular markings should be compared with cardiac size. If a large volume left-to-right shunt exists, the heart size has to be larger than normal. Pulmonary vascular markings may be more difficult to analyze from portable films obtained in a neonatal care unit because the X-ray exposure time is longer, resulting in blurred images from rapid respirations, and from the redistributed pulmonary blood volume in the supine patient. With experience obtained from viewing a number of chest X-rays, the status of pulmonary vasculature can be judged. With increased vascularity, the lung fields show increased pulmonary arterial markings, the hilae are plump, and vascular shadows radiate toward the periphery. With decreased vascularity, the lungs appear dark or lucent; the hilum is small; and the pulmonary arterial vessels are stringy. Summary of chest X-ray parameters Situs (heart, stomach, and aortic arch) Cardiac size Cardiothymic silhouette, shape, and contour Pulmonary artery silhouette Pulmonary vascular markings (normal, increased, or decreased; symmetric versus asymmetric) Pulse oximetry Because oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin absorb light differently, spectrophotometry can be used to measure the percentage of hemoglobin bound to oxygen. Other factors that affect pulse oximeter results include skin pigmentation, poor skin perfusion, tachycardia, ambient light, and shifts in the oxyhemoglobin absorption spectrum that can accompany chronic cyanosis. Blood counts In infants and children with cyanotic forms of congenital cardiac disease, hypoxemia stimulates the bone marrow to produce more red blood cells (polycythemia), thus improving oxygen-carrying capacity. As a result, both the total number of erythrocytes and the hematocrit are elevated. The production of the increased red cell mass should be paralleled by an increase in hemoglobin. In a patient with cyanosis and normal iron stores, the hemoglobin also should be elevated so that the red-cell indices are normal. Iron deficiency In infancy, iron deficiency is common; it may be accentuated in cyanotic infants because of the increased iron requirements and by the fact that such infants may have a poor appetite and primarily a milk diet. In such infants, the red-cell indices reflect iron deficiency anemia because the hemoglobin value is low relative to the red blood cell count and the hematocrit. In fact, a cyanotic infant may have a hemoglobin value that is normal or even elevated for age and still have iron deficiency. The hematocrit value reflects the volume of red cells elevated in response to hypoxemia; the hemoglobin value primarily reflects the amount of iron available for its formation.
The P-wave axis changes when the pacemaker initiating atrial depolarization is abnormally located managing diabetes 33 quality 60caps diabecon. One example is mirror-image dextrocardia associated with situs inversus blood glucose below 60 buy generic diabecon on line, in which the anatomic right atrium and the sinoatrial node are located on the left side diabetes mellitus test questions purchase 60caps diabecon overnight delivery, so atrial depolarization occurs from left to right diabetes mellitus kidney generic 60caps diabecon free shipping. Because most of the right atrium is depolarized before the left atrium, the early portion of the P wave is accentuated in right atrial enlargement. When longer, left atrial enlargement or intra-atrial block (much rarer) is present. Relationship of limb leads in frontal plane (a) and precordial leads in horizontal plane (b). Ventricular depolarization starts on the left side of the interventricular septum near the base and proceeds across the septum from left to right. The posterior basilar part of the left ventricle and the infundibulum of the right ventricle are the last portions of ventricular myocardium to be depolarized. In children, the axis varies because of the hemodynamic and anatomic changes that occur with age. Right-axis deviation is almost always associated with right ventricular hypertrophy or enlargement. Left-axis deviation is associated with myocardial disease or ventricular conduction abnormalities, such as those that occur in atrioventricular septal defect, but uncommonly with isolated left ventricular hypertrophy. Leads V1 and V6 should each exceed 8 mm; if smaller, pericardial effusion or similar conditions may be present. The term ventricular hypertrophy is partly a misnomer, as it applies to electrocardiographic patterns in which the primary anatomic change is ventricular chamber enlargement and to patterns associated with cardiac conditions in which the ventricular walls are thicker than normal. This usually leads to right-axis 46 Pediatric cardiology deviation, a taller than normal R wave in lead V1, and a deeper than normal S wave in lead V6. Right ventricular hypertrophy can be diagnosed by either of the following criteria: (a) the R wave in lead V1 is greater than normal for age or (b) the S wave in lead V6 is greater than normal for age. A positive T wave in lead V1 in patients between the ages of 7 days and 10 years supports the diagnosis of right ventricular hypertrophy. Left ventricular hypertrophy can be diagnosed by this "rule of thumb": (a) an R wave in lead V6 > 25 mm (or >20 mm in children less than 6 months of age) and/or (b) an S wave in lead V1 > 25 mm (or >20 mm in children less than 6 months of age) (Figure 1. Distinction between left ventricular hypertrophy and left ventricular enlargement is difficult. Left ventricular hypertrophy may show a deep S wave in lead V1 and a normal amplitude R wave in lead V6, whereas left ventricular enlargement shows a tall R wave in lead V6 associated with a deep Q wave and a tall T wave. The electrocardiographic standards presented are merely guidelines for interpretation. The electrocardiograms of a few normal patients may be interpreted as ventricular hypertrophy, and indeed, with utilization of these standards only, the electrocardiograms of some patients with heart disease and anatomic hypertrophy may not be considered abnormal. In complete right bundle branch block, an rsR pattern appears in lead V1 and the R is wide. Right bundle branch block frequently results from operative repair of tetralogy of Fallot. The Q waves should be carefully analyzed; abnormal Q waves may be present in patients with myocardial infarction. Normally, the Q wave represents primarily depolarization of the interventricular septum. After the initial 20 ms of the 48 Pediatric cardiology ventricular depolarization, the left ventricular free wall begins to depolarize. With left ventricular infarction, the right ventricular depolarization is unopposed and directed rightward. Whereas ventricular depolarization takes place from the endocardium to the epicardium, repolarization is considered to occur in the opposite direction.
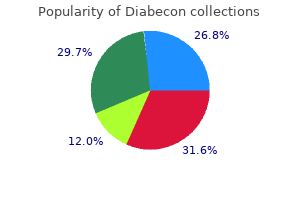
The term imprinting is used to describe the phenomenon by which certain genes function differently managing diabetes at everyday health buy diabecon 60 caps on-line, depending on whether they are maternally or paternally derived diabetes signs in adults effective diabecon 60 caps. The imprint lasts for one generation and is then removed managing diabetes with diet and exercise purchase diabecon 60 caps line, so that an appropriate imprint can be re-established in the germ cells of the next generation blood sugar vertigo discount diabecon 60 caps. The effects of imprinting can be observed at several levels: that of the whole genome, that of particular chromosomes or chromosomal segments, and that of individual genes. For example, the effect of triploidy in human conceptions depends on the origin of the additional haploid chromosome set. When paternally derived, the placenta is large and cystic with molar changes and the fetus has a large head and small body. When the extra chromosome set is maternal, the placenta is small and underdeveloped without cystic changes and the fetus is noticeably underdeveloped. An analogous situation is seen in conceptions with only a maternal or paternal genetic contribution. Androgenic conceptions, arising by replacement of the female pronucleus with a second male pronucleus, give rise to hydatidiform moles which lack embryonic tissues. Gynogenetic conceptions, arising by replacement of the male pronucleus with a second female one, results in dermoid cysts that develop into multitissue ovarian teratomas. Angelman syndrome is quite distinct and is associated with severe mental retardation, microcephaly, ataxia, epilipsy and absent speech. Similar de novo cytogenetic or molecular deletions can be detected in both conditions. Uniparental disomy is rare in Angelman syndrome, but when it occurs it involves disomy of the paternal chromosome 15. Mosaicism may involve whole chromosomes or single gene mutations and is a postzygotic event that arises in a single cell. Once generated, the genetic change is transmitted to all daughter cells at cell division, creating a second cell line. The process can occur during early embryonic development, or in later fetal or postnatal life. The time at which the mosaicism develops will determine the relative proportions of the two cell lines, and hence the severity of the phenotype caused by the abnormal cell line. Chimaeras have a different origin, being derived from the fusion of two different zygotes to form a single embryo. Functional mosaicism occurs in all females as only one X chromosome remains active in each cell. Thus, alleles that differ between the two chromosomes will be expressed in mosaic fashion.
Buy diabecon 60caps with mastercard. Reversing type 2 diabetes in the real world by Dr David Cavan | PHC Conference 2018.
Diseases
- Dengue fever
- Tracheophageal fistula hypospadias
- Patterson Stevenson syndrome
- Fetal akinesia syndrome X linked
- Goodpasture pneumorenal syndrome
- Achondroplastic dwarfism
- Seemanova syndrome type 2