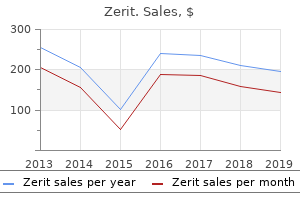
"Buy cheap zerit 40mg line, medicine 9312".
By: K. Curtis, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Vice Chair, Georgetown University School of Medicine
Influenza vaccination of health care workers in long-term-care hospitals reduces the mortality of elderly patients medicine 6 year effective 40mg zerit. Public health and aging: influenza vaccination coverage among adults aged 50 years and pneumococcal vaccination coverage among adults aged 65 years-United States symptoms quad strain best buy for zerit, 2002 medicine x xtreme pastillas generic zerit 40 mg with amex. Influenza and pneumococcal vaccination coverage among persons aged 65 years and persons aged 1864 years with diabetes or asthma-United States medicine 4h2 pill cost of zerit, 2003. Facilitating influenza and pneumococcal vaccination through standing orders programs. Zanamivir prophylaxis: an effective strategy for the prevention of influenza types A and B within households. Management of influenza in households: a prospective, randomized comparison of oseltamivir treatment with or without postexposure prophylaxis. An outbreak of multidrugresistant pneumococcal pneumonia and bacteremia among unvaccinated nursing home residents. Azithromycin prophylaxis during a hospital outbreak of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Experiences with influenza-like illness and attitudes regarding influenza prevention-United States, 200304 influenza season. Vidya G Doddawad Associate Professor Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology 1-6 2 4 1 Dr. Abstract the antibiotics are used in the management of life threatening infections since many decades. The antibiotics are indispensable drugs in the management of oral &maxillofacial infections. Over the years, several new concepts are been formulated in the principles of antibiotic therapy. This review article we will discuss about the current principles in the antibiotic therapy for management oral & maxillofacial infections. Historically, the term antibiotic referred to antimicrobial drugs produced by living organisms (bacteria or fungi) because of their natural metabolism, where as chemotherapeutic referred only to artificial prepared antimicrobial agents. Today all natural antibiotic are chemically modified (semi synthetic) to improve their pharmacokinetic properties, making the distinction between antibiotics and chemotherapeutic agents obsolete. The current trend is to use the words antibiotic and antimicrobial agent for all antimicrobial drugs, regardless of their origin. The use antimicrobial agent is based on selective toxicity, which means that they severely damage microorganisms but, ideally, have no effect on eukaryotic cells (human cells). Most of the dental surgical treatments involve use of antibiotics to prevent or treat infections. A thorough knowledge about the antibiotics is very much essential in our dental practice for successful dental treatment. In this article, we will discuss about the proper use of the antibiotics in our dental practice. Understanding antibiotics: Antibiotics are used inappropriately in 75% of cases involving dental conditions. When clinical examination of the patient reveals presence of infection As a prophylactic therapy 2. Control the severity and complications of infection As a prophylactic Antibiotics should be used only in the presence of infection. The dental surgeon should take a detail history and thorough systemic, local & radiographic examination to diagnose the disease as infection. In addition, one should do hematologic, serologic & other laboratory examination whenever necessary to diagnose & to evaluate the origin or severity of oral & maxillofacial infection. The human defense mechanism fights against the invading pathogens causing infection. This involves cellular defense mechanism and non-cellular defense mechanism involving several enzymes, proteins and other chemical agents synthesized by the body. Antibiotics are used in the management of infections to control the severity of infection and to prevent complications of infections. Antibiotic prophylaxis is the administration of antibiotics to patients who have no known infection for the purpose of preventing microbial colonization and reducing the potential for postoperative complications. Principles of antibiotic prophylaxis Benefits from prophylaxis outweigh the risks of antibiotic-related allergy, toxicity, super infection, and the development of drug-resistant microbial srains.
Troughs of 15-20 mcg/mL are indicated for patients being treated for documented or suspected Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections medicine identifier generic zerit 40 mg amex, endocarditis medicine hat mall 40mg zerit sale, pneumonia treatment for scabies discount 40 mg zerit free shipping, meningitis medications related to the female reproductive system order zerit cheap online, and osteoarticular infections. Concentration-toxicity Relationship Shortly following the release of vancomycin to the market in 1956, reports began to surface describing ototoxicity secondary to vancomycin therapy, with serum concentrations ranging from 806 100 mcg/mL. Based on this, the authors recommended therapeutic drug monitoring of vancomycin to reduce the risk of ototoxicity. This side effect, however, has been seen in only 2% of patients who 15 receive vancomycin. Cantu and colleagues performed a literature search that yielded 53 reported 7 cases of ototoxicity over a 30-year period. Of these cases, only 17 were patients receiving monotherapy, all of which were reversible. Vancomycin levels ranged from 17-62 mcg/mL, so no specific threshold level was found. Vancomycin-associated ototoxicity is manifested by vestibular 8 damage and/or cochlear damage, which leads to sensory hearing loss and tinnitis. This effect, however, seems to be relatively rare when vancomycin is used as monotherapy. The incidence of nephrotoxicity secondary to vancomycin monotherapy is estimated to be 5-7% but increases to 43% 7,8 in patients receiving concomitant nephrotoxic drugs. When reviewing cases, it is difficult to establish with certainty whether vancomycin is the cause of impaired renal function or whether vancomycin accumulation has occurred as a consequence of 9 decreased renal function for other reasons. Many of the early reported cases of nephrotoxicity occurred with impure preparations of vancomycin. Modern formulations have excellent safety profiles; however, reports of vancomycin-related nephrotoxicity still surface, particularly with the recommendations to increase vancomycin trough concentrations 4 from the typical range of 5-15 mg/L to 10-20 mg/L. Studies have been performed trying to establish a link between higher vancomycin trough concentrations and the risk for nephrotoxicity. Four recent studies found a greater risk of 11-14 nephrotoxicity at trough levels 15 mcg/mL as compared to trough levels less than 15 mcg/mL. However, the causal relationship is difficult to discern from these studies because of small sample sizes, retrospective study design (for all but one), and a number of potential confounding factors including concomitant nephrotoxins. Another recent study has identified the total daily dose as a potential factor in nephrotoxicity, suggesting that daily doses of 4g or more are significantly associated with an increased risk of nephrotoxicity, even after controlling for potential confounding 15 factors in a multivariate analysis. Concentration-efficacy Relationship Vancomycin has been shown to demonstrate concentration-independent killing against Grampositive pathogens. A consensus paper on therapeutic monitoring of vancomycin recommends vancomycin trough concentrations always be maintained above 10 mcg/mL and between 15-20 mcg/mL for complicated infections. Kullar et al found that failing to obtain a first trough concentration of at least 15 mcg/mL was independently associated with higher rates of 23 treatment failure. Sampling considerations Justification for monitoring peak concentrations with vancomycin is lacking for most populations. If peak concentrations are obtained, a few points must be kept in mind: (1) Vancomycin pharmacokinetics have been described by 1, 2 and 3 compartmental models; (2) the vancomycin concentration at 1 hr may be more than double that taken at 2 hr and still be within the 16 recommended target range; (3) To get accurate levels, one must be certain that the distribution phase is complete before the peak serum level is drawn. In order to interpret peak levels appropriately, the exact infusion time and exact draw time for the lab must be documented and reported. Given that peak levels have not been clearly correlated with efficacy or toxicity, abandoning the measurement of peak vancomycin concentrations would eliminate the confusion surrounding their interpretation. Furthermore, Sanders has suggested that, provided the trough concentration is within recommended limits, the peak level is unlikely to reach a potentially toxic 20 range. Serum Drug Levels Drug Vancomycin Trough Time to Obtain Therapeutic Range Hospital Cost Ґ Ѕ hour before infusion 10-20 mcg/mL $9. Keep in mind that the infusion rate for vancomycin is 1g/hr, so large doses may require long infusion periods. Because vancomycin exhibits linear pharmacokinetics, increases or decreases in total daily dose have a corresponding proportional increase or decrease in trough values. Set up a proportional relationship to estimate the actual trough based on new dose. Cmin(actual) x = Current total daily dose New total daily dose x = estimated new trough based on new dose Ex. Note: Altering the dosing frequency will have larger effects on the resulting trough than suggested by the proportion. For example, if in the above example the dosing frequency (and not the dose) was changed to q8h (this results in the same 50% increase in total daily dose), then the resulting trough would be higher than 16.
Cheap zerit 40 mg with amex. MS Symptoms and Brain Lesions Gone.
Page 203 of 388 Malaria Infectious Diseases of Panama - 2013 edition Graph: Panama symptoms 1974 purchase zerit. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: aerobic gram-negative bacillus (virtually all cases) Human None Endogenous Variable Culture of otic exudate and biopsy material medications 563 order 40 mg zerit with visa. Clinical the case definition of Malignant Otitis Externa consists of pain medicine dictionary cheap zerit 40 mg amex, edema treatment trichomonas 40 mg zerit fast delivery, exudate, granulations, microabscesses (when 1 explored), positive bone scan or failure of local treatment often more than 1 week. Severe pain and tenderness in the mastoid area are accompanied by drainage of pus from the external canal. Phasmidea, Filariae: Mansonella ozzardi Human Fly (black fly = Simulium) or midge (Culicoides) None 5m - 18m (range 1m - 2y) Identification of microfilariae in skin snips or blood. Filaria ozzardi, Mansonella ozzardi, Microfilaria bolivarensis, Ozzardiasis, Tetrapetalonema ozzardi. Nummular keratitis, associated with the presence of microfilaria in the cornea, is 1-3 common. Phasmidea, Filariae: Mansonella (Esslingeria) perstans Human Midge (Culicoides spp. Acanthocheilonema perstans, Bung eye disease, Dipetalonema berghei, Dipetalonema perstans, Dipetalonema semiclarum, Esslingeria perstans, Filaria perstans, Mansonella perstans, Mansonella rhodhaini, Mansonella semiclarum, Meningonema peruzzii, Tetrapetalonema berghei, Tetrapetalonema perstans. Supportive As for adult Consider in a forest worker with headache, myalgia, arthralgia, lymphadenopathy and a maculopapular rash; although acute illness resolves within 5 days, joint pains may persist for months. Paramyxoviridae, Paramyxovirinae, Morbillivirus: Measles virus Human None Droplet 8d - 14d Viral culture (difficult and rarely indicated). Masern, Massling, Mazelen, Meslinger, Morbilli, Morbillo, Rubeola, Rugeole, Sarampion, Sarampo. Laboratory criteria for diagnosis · At least a fourfold increase in antibody titer or · Isolation of measles virus or · Presence of measles-specific IgM antibodies Case classification · Clinically confirmed: A case that meets the clinical case definition. Acute illness: Symptoms begin to appear about 10 to 12 days after exposure to the virus, with fever followed by cough, rhinorrhea, and/or 1 conjunctivitis. Complications: 3 4 Complications of measles include diarrhea, otitis media (10%), pneumonia (5%), encephalitis (0. Page 210 of 388 Measles Infectious Diseases of Panama - 2013 edition · Measles is the leading cause of blindness among African children, as a result of concomitant vitamin A deficiency. Page 211 of 388 Measles Infectious Diseases of Panama - 2013 edition Graph: Panama. Notable outbreaks: 2011 - An outbreak (3 cases) in Panama included an index patient who had acquired measles in Europe. Burkholderia pseudomallei An aerobic gram-negative bacillus Soil None Water: Contact, ingestion, aerosol Breast milk (rare) 3d - 21d (range 2d - 1y) Culture of blood, sputum, tissue. May present as: lymphangitis with septicemia; or fever, cough and chest pain; or diarrhea; bone, central nervous system, liver and parotid infection are occasionally encountered; case-fatality rate 10% to over 50% (septicemic form). Other predisposing conditions include collagen-vascular disease, alcoholism, malnutrition, chronic renal or hepatic disease, corticosteroid therapy, splenectomy, pregnancy, chronic granulomatous disease, leukemia and lymphoma. Acute melioidosis can be divided into five clinical forms: · septicemia without abscess formation · septicemia with disseminated foci · localized infection · transitory bacteremia · "fever of unknown origin" Most patients with overt infection present with pneumonia which may include pulmonary nodules, consolidation, necrotizing 11-13 lesions, pleural effusion, pleural thickening and mediastinal abscesses. Page 213 of 388 Melioidosis Infectious Diseases of Panama - 2013 edition epididymo-orchitis, prostatitis, suppurative parotitis, mycotic aneurysm, parapharyngeal abscess, corneal 47-49 50 51 52-54 ulcer, necrotizing fasciitis, septic arthritis, psoas and other muscular abscesses. Renal failure occurs in up to one-third of hospitalized patients with melioidosis, and carries a poor prognosis. In nonendemic regions, patients present with reactivated disease occurring months to years after initial exposure to the organism. Aseptic meningitis, Encephalitis - viral, Meningite virale, Meningitis, viral, Meningo-encefalite virale, Viral encephalitis, Viral meningitis. As a group, the viral meningitides are characterized by fever, headache, meningismus and lymphocytic pleocytosis. Page 215 of 388 Meningitis - aseptic (viral) Infectious Diseases of Panama - 2013 edition References 1. Bactericidal agent(s) appropriate to known or suspected pathogen + dexamethasone As for adult H. Case classification · Potential: (bacterial meningitis case): a child with a clinical syndrome consistent with bacterial meningitis. As a group, the bacterial meningitides are characterized by signs of sepsis, fever, headache, meningismus and neutrophilic 1 2 pleocytosis. Meningitis - bacterial in Panama 76 cases of bacterial meningitis were reported for the age group 2 months to 15 years during 1992 to 1993: 61% Haemophilus influenzae-b, 13% pneumococcal, 18% meningococcal.
Isolates may be stored at -80°C in Lab Lemco broth supplemented with 10% glycerol medicine natural generic zerit 40mg with mastercard. For marine organisms use marine broth 2216 supplemented with 30% glycerol (Bowman and Nichols treatment neutropenia generic 40 mg zerit free shipping, 2002) symptoms lupus order zerit mastercard. One method is to suspend organisms in 1 ml of inositol horse serum in Wheaton serum bottles or appropriate container depending on freeze-drying equipment medicine zalim lotion cheap zerit 40 mg without a prescription. Snap freeze in liquid nitrogen and follow instructions for freeze-drying equipment (see Chapter 7). However, phenotypic tests would need to be carried out to differentiate from atypical A. The aerolysin gene is considered to be a useful virulence marker for detecting virulent pathogenic Aeromonas species (Kong et al. However, most, if not all, of these primers will undergo a long period of validation before they are routine in a diagnostic laboratory (Bader et al. Each forward and reverse primer is listed together with the recommended annealing temperature, number of cycles and expected product length in base pairs. Differences in nucleotide sequence divided the species of Edwardsiella into a pathogenic and non-pathogenic cluster. Three separate forward primers are available, with genomovars 1 and 3 having the same reverse primer (see Table 6. Primers for amplifying genomovar 2 produce a product band at 621 bp, but also produce bands at 800 and 1000 bp in all Flavobacterium species (Triyanto et al. There is some doubt as to the specificity of some of the primers for Vibrio parahaemolyticus and V. The toxR gene, which is involved in the regulation of many genes, is conserved amongst the Vibrio species; however, there is a low degree of homology that allows for selection of species-specific primers. Thermocycling conditions were also standardized with an initial denaturation step of 95°C for 4 min, followed by 30 cycles of 95°C for 45 s, annealing for 45°C for universal primers and 55°C for specific primers, with an extension of 72°C for 90 s. A final cycle of 4°C infinity was used as a holding cycle (Taylor and Winton, 2002). This method is also suitable for tissue samples with an overnight incubation in digestion buffer followed by sonication (Goldenberger et al. There are many methods available for both manual and commercially available methods. To 100 ml of homogenized tissue add 100 ml of Chelex-100 resin (Bio-Rad Laboratories or Sigma-Aldrich). Too much or too little of any of these reagents will cause nonspecific background, mispriming or insufficient product generated. However, not more than 2% should be used, as greater than this concentration is inhibitory to Taq. When a different number of samples are tested then the master mix is easily calculated. Resuspend pellet in 50 ml of water, then dilute 1:10 with 1% Triton-X-100 and place in boiling waterbath for 5 min. Thermocycling conditions the cycling conditions will depend on the type of thermocycler, the annealing temperature of the primers and the type of Taq enzyme used, whether it is a hot-start enzyme or not. Then, 2535 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 30 s, annealing at 5568°C 30 s, extension at 72°C for 30 s. A final cycle is suggested as for the last cycle but with an extension time of 10 min. The Tm can be estimated by calculating 2°C for A or T, and 4°C for G or C in the primer sequence. A lower than optimal annealing temperature may lead to mispriming of non-target sequence or the misextension of incorrect nucleotides at the 3 end of the primers. The recommended number of cycles per starting material is 2530 (for 3 Ч 105 target molecules), 3035 (1. Gel electrophoresis A standard gel for the detection of amplified product is as follows. The gel is stained for 1 h in 1 litre of distilled water containing 50 ml of ethidium bromide. Ethidium bromide is a carcinogen and therefore appropriate precautions need to be taken, such as wearing lab coats and gloves.